Python量化数据仓库搭建系列2:Python操作数据库
Python量化数据仓库搭建系列2:Python操作数据库
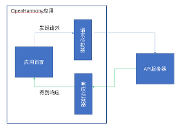
本系列教程为量化开发者,提供本地量化金融数据仓库的搭建教程与全套源代码。我们以恒有数(UDATA)金融数据社区为数据源,将金融基础数据落到本地数据库。教程提供全套源代码,包括历史数据下载与增量数据更新,数据更新任务部署与日常监控等操作。
在上一节讲述中,我们选择了MySQL作为本系列教程的数据库,故本文着重讲解Python操作MySQL的步骤,并封装方法。在文末简单介绍Python操作MongoDB、SQLite、PostgreSQL数据库;
一、pymysql用法
1、安装pymysql模块
pip install pymysql
2、连接数据库
from pymysql import * # 打开数据库连接,数据库参数可以在MySQL界面或数据库配置文件中查看 conn = pymysql.connect(host = '数据库IP', port = '端口', user = '用户名', password = '密码', database='数据库名称') # 使用 cursor() 方法创建一个游标对象 cursor cursor = conn.cursor() # 在数据库操作执行完毕后,关闭数据库连接 # conn.close()
3、常见SQL代码执行
from pymysql import * # 执行SQL代码:建表、删表、插入数据 def Execute_Code(sql_str): # 打开数据库连接 conn = pymysql.connect(host = '127.0.0.1',port = 3306,user = 'root', password = '密码',database='udata') # 使用 cursor() 方法创建一个游标对象 cursor cursor = conn.cursor() try: # 使用execute()方法执行SQL cursor.execute(sql) # 提交到数据库执行 conn.commit() except: # 发生错误时回滚 conn.rollback() # 关闭数据库连接 conn.close()
A、建表
sql_str = '''CREATE TABLE TB_Stock_List_Test ( secu_code CHAR(20), hs_code CHAR(20), secu_abbr CHAR(20), chi_name CHAR(40), secu_market CHAR(20), listed_state CHAR(20), listed_sector CHAR(20), updatetime CHAR(20));''' Execute_Code(sql_str)
B、插入数据
sql_str = '''
INSERT INTO TB_Stock_List_Test
(`secu_code`,`hs_code`,`secu_abbr`,`chi_name`,`secu_market`,`listed_state`
,`listed_sector`,`updatetime`)
VALUES
('000001','000001.SZ','平安银行','平安银行股份有限公司','深圳证券交易所','上市',
'主板','2021-10-25 20:10:55');
'''
Execute_Code(sql_str)C、更新数据
sql_str = "UPDATE tb_stock_list SET updatetime = '2021-10-30 20:10:55' " Execute_Code(sql_str)
D、删除数据
sql_str = 'DELETE FROM tb_stock_list' Execute_Code(sql_str)
E、删除表格
sql_str = 'DROP TABLE IF EXISTS tb_stock_list' Execute_Code(sql_str)
4、查询操作
def Select_Code(sql_str): # 打开数据库连接 conn = pymysql.connect(host = '127.0.0.1',port = 3306,user = 'root', password = '密码',database='udata') # 使用 cursor() 方法创建一个游标对象 cursor cursor = conn.cursor() # 使用execute()方法执行SQL cursor.execute(sql_str) # 获取所有记录列表 results = cursor.fetchall() # 关闭数据库连接 conn.close() return results
sql_str = 'select * from tb_stock_list' results = Select_Code(sql_str) results
5、方法封装
将上述用法,封装为自定义类,存为MySQLOperation.py文件,代码如下:
from pymysql import * # MySQL操作函数 class MySQLOperation: def __init__(self, host, port, db, user, passwd, charset='utf8'): # 参数初始化 self.host = host self.port = port self.db = db self.user = user self.passwd = passwd self.charset = charset def open(self): # 打开数据库连接 self.conn = connect(host=self.host,port=self.port ,user=self.user,passwd=self.passwd ,db=self.db,charset=self.charset) # 使用 cursor() 方法创建一个游标对象 cursor self.cursor = self.conn.cursor() def close(self): # 断开数据库连接 self.cursor.close() self.conn.close() def Execute_Code(self, sql): # 执行SQL代码:建表、删表、插入数据 try: self.open() # 打开数据库连接 self.cursor.execute(sql) # 使用execute()方法执行SQL self.conn.commit() # 提交到数据库执行 self.close() # 断开数据库连接 except Exception as e: self.conn.rollback() # 发生错误时回滚 self.close() # 断开数据库连接 print(e) def Select_Code(self, sql): # 执行SQL代码,查询数据 try: self.open() # 打开数据库连接 self.cursor.execute(sql) # 使用execute()方法执行SQL result = self.cursor.fetchall() # 获取所有记录列表 self.close() # 断开数据库连接 return result # 返回查询数据 except Exception as e: self.conn.rollback() # 发生错误时回滚 self.close() # 断开数据库连接 print(e)
插入与查询用法如下,其余用法类似,此处不再赘述;
import pandas as pd
host='127.0.0.1'
port=3306
user='root'
passwd="密码"
db='udata'
# 方法实例化
MySQL = MySQLOperation(host, port, db, user, passwd)
# 插入操作代码
sql_str = '''
INSERT INTO tb_stock_list
(`secu_code`,`hs_code`,`secu_abbr`,`chi_name`,`secu_market`,`listed_state`,`listed_sector`,`updatetime`)
VALUES
('000001','000001.SZ','平安银行','平安银行股份有限公司','深圳证券交易所','上市',
'主板','2021-10-25 20:15:55');
'''
MySQL.Execute_Code(sql_str)
# 查询数据
sql_str = 'select * from tb_stock_list'
results = MySQL.Select_Code(sql_str)
results二、sqlalchemy用法
由于上述pymysql用法已经可以满足大部分使用需求,sqlalchemy实现功能与之类似。这里着重介绍一下基于sqlalchemy链接数据库的pandas.to_sql和pandas.read_sql操作。
1、安装pymysql模块
pip install sqlalchemy
2、连接数据库
from sqlalchemy import create_engine
host='127.0.0.1'
port = 3306
user='root'
password='密码'
database='udata'
engine = create_engine('mysql://{0}:{1}@{2}:{3}/{4}?charset=utf8'.format(user
,password
,host
,port
,database))3、pandas.to_sql
将DataFrame中的数据,写入MySQL数据库,代码示例如下:
import pandas as pd # 定义需要写入的数据,DataFrame格式 data = pd.DataFrame([['000001','000001.SZ','平安银行','平安银行股份有限公司' ,'深圳证券交易所','上市','主板','2021-10-25 20:12:55'], ['000002','000002.SZ','万 科A','万科企业股份有限公司' ,'深圳证券交易所','上市','主板','2021-10-25 20:12:55']]) # 列名赋值 data.columns = ['secu_code','hs_code', 'secu_abbr', 'chi_name' , 'secu_market', 'listed_state','listed_sector','updatetime'] # 写入数据库 data.to_sql(name='tb_stock_list', con=engine, index=False, if_exists='append')
if_exists 参数用于当目标表已经存在时的处理方式,默认是 fail,即目标表存在就失败。另外两个选项是 replace 表示替代原表,即删除再创建,append 选项仅添加数据。
4、pandas.read_sql
从数据库中,将数据读取为DataFrame,代码示例如下:
# 将sql查询结果,赋值为result
result = pd.read_sql('''SELECT * FROM tb_stock_list ''', con=engine)
result三、Python操作其他常见数据库
1、MongoDB
(1)安装pymongo:pip install pymongo
(2)操作简介
import pymongo
# 连接MongoDB
conn = pymongo.MongoClient(host='localhost',port=27017
,username='username', password='password')
# 指定数据库
db = conn['udata'] # db = client.udata
# 指定集合
collection = db['tb_stock_list'] # collection = db.tb_stock_list
# 插入数据 insert_one()、insert_many()
data1 = {} # 集合,键值对,1条数据
data2 = {} # 集合,键值对,1条数据
result = collection.insert_many([data1, data2])
# result = collection.insert_one(data1)
# 查询数据 find_one()、find()
result = collection.find_one({'secu_code': '000001'})
# 更新数据 update_one()、update()
result = collection.update_one({'secu_code': '000001'}, {'$set': {'hs_code': '000001'}})
# 删除数据 remove()、delete_one()和delete_many()
result = collection.remove({'secu_code': '000001'})2、SQLite
(1)安装sqlite3:pip install sqlite3
(2)操作简介
import sqlite3
# 连接数据库
conn = sqlite3.connect('udata.db')
# 创建游标
cursor = conn.cursor()
# 执行SQL
sql = "增减删等SQL代码"
cursor.execute(sql)
# 查询数据
sql = "查询sql代码"
values = cursor.execute(sql)
# 提交事物
conn.commit()
# 关闭游标
cursor.close()
# 关闭连接
conn.close()3、PostgreSQL
(1)安装psycopg2:pip install psycopg2
(2)操作简介
import psycopg2 # 连接数据库 conn = psycopg2.connect(database="udata", user="postgres" , password="密码", host="127.0.0.1", port="5432") # 创建游标 cursor = conn.cursor() # 执行SQL sql = "增减删等SQL代码" cursor.execute(sql) # 查询全部数据 sql = "查询sql代码" cursor.execute(sql) rows = cursor.fetchall() # 事物提交 conn.commit() # 关闭数据库连接 conn.close()
综上,Python操作数据库的简要介绍就结束了;还有很多类型的数据库,Python操作它们的过程大同小异,后续我也将会继续梳理相关资料。
下一节《Python量化投资数据仓库搭建3:数据落库代码封装》
|
- 上一条: 保姆级教程!将 Vim 打造一个 IDE (Python 篇) 2021-10-27
- 下一条: Loguru:Python 日志终极解决方案 2021-11-04
相关文章
- 高并发先操作数据库,还是先操作缓存?5 个方案告诉你! 2021-08-10
- 送你一个Python 数据排序的好方法 2021-09-27
- 【Python】爬虫实战,零基础初试爬虫下载图片 2021-07-25
- 教你用Python 编写 Hadoop MapReduce 程序 2021-09-18
- 超详细1小时学会Python,有了这篇文章,就入行了 2021-07-20
热度排行