手写 Vue2 系列 之 编译器
当学习成为了习惯,知识也就变成了常识。 感谢各位的 关注、点赞、收藏和评论。
新视频和文章会第一时间在微信公众号发送,欢迎关注:李永宁lyn
文章已收录到 github 仓库 liyongning/blog,欢迎 Watch 和 Star。
封面

前言
接下来就要正式进入手写 Vue2 系列了。这里不会从零开始,会基于 lyn-vue 直接进行升级,所以如果你没有阅读过 手写 Vue 系列 之 Vue1.x,请先从这篇文章开始,按照顺序进行学习。
都知道,Vue1 存在的问题就是在大型应用中 Watcher 太多,如果不清楚其原理请查看 手写 Vue 系列 之 Vue1.x。
所以在 Vue2 中通过引入了 VNode 和 diff 算法来解决该问题。通过降低 Watcher 的粒度,一个组件对应一个 Watcher(渲染 Watcher),这样就不会出现大型页面 Watcher 太多导致性能下降的问题。
在 Vue1 中,Watcher 和 页面中的响应式数据一一对应,当响应式数据发生改变,Dep 通知 Watcher 完成对应的 DOM 更新。但是在 Vue2 中一个组件对应一个 Watcher,当响应式数据发生改变时,Watcher 并不知道这个响应式数据在组件中的什么位置,那又该如何完成更新呢?
阅读过之前的 源码系列,大家肯定都知道,Vue2 引入了 VNode 和 diff 算法,将组件 编译 成 VNode,每次响应式数据发生变化时,会生成新的 VNode,通过 diff 算法对比新旧 VNode,找出其中发生改变的地方,然后执行对应的 DOM 操作完成更新。
所以,到这里大家也能明白,Vue1 和 Vue2 在核心的数据响应式部分其实没什么变化,主要的变动在编译器部分。
目标
完成 Vue2 编译器的一个简版实现,从字符串模版解析开始,到最终得到 render 函数。
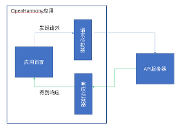
编译器
在手写 Vue1 时,编译器时通过 DOM API 来遍历模版的 DOM 结构来完成的,在 Vue2 中不再使用这种方式,而是和官方一样,直接编译组件的模版字符串,生成 AST,然后从 AST 生成渲染函数。
首先将 Vue1 的 compiler 目录备份,然后新建一个 compiler 目录,作为 Vue2 的编译器目录
mv compiler compiler-vue1 && mkdir compiler
mount
/src/compiler/index.js
/**
* 编译器
*/
export default function mount(vm) {
if (!vm.$options.render) { // 没有提供 render 选项,则编译生成 render 函数
// 获取模版
let template = ''
if (vm.$options.template) {
// 模版存在
template = vm.$options.template
} else if (vm.$options.el) {
// 存在挂载点
template = document.querySelector(vm.$options.el).outerHTML
// 在实例上记录挂载点,this._update 中会用到
vm.$el = document.querySelector(vm.$options.el)
}
// 生成渲染函数
const render = compileToFunction(template)
// 将渲染函数挂载到 $options 上
vm.$options.render = render
}
}compileToFunction
/src/compiler/compileToFunction.js
/**
* 解析模版字符串,得到 AST 语法树
* 将 AST 语法树生成渲染函数
* @param { String } template 模版字符串
* @returns 渲染函数
*/
export default function compileToFunction(template) {
// 解析模版,生成 ast
const ast = parse(template)
// 将 ast 生成渲染函数
const render = generate(ast)
return render
}parse
/src/compiler/parse.js
/**
* 解析模版字符串,生成 AST 语法树
* @param {*} template 模版字符串
* @returns {AST} root ast 语法树
*/
export default function parse(template) {
// 存放所有的未配对的开始标签的 AST 对象
const stack = []
// 最终的 AST 语法树
let root = null
let html = template
while (html.trim()) {
// 过滤注释标签
if (html.indexOf('<!--') === 0) {
// 说明开始位置是一个注释标签,忽略掉
html = html.slice(html.indexOf('-->') + 3)
continue
}
// 匹配开始标签
const startIdx = html.indexOf('<')
if (startIdx === 0) {
if (html.indexOf('</') === 0) {
// 说明是闭合标签
parseEnd()
} else {
// 处理开始标签
parseStartTag()
}
} else if (startIdx > 0) {
// 说明在开始标签之间有一段文本内容,在 html 中找到下一个标签的开始位置
const nextStartIdx = html.indexOf('<')
// 如果栈为空,则说明这段文本不属于任何一个元素,直接丢掉,不做处理
if (stack.length) {
// 走到这里说说明栈不为空,则处理这段文本,并将其放到栈顶元素的肚子里
processChars(html.slice(0, nextStartIdx))
}
html = html.slice(nextStartIdx)
} else {
// 说明没有匹配到开始标签,整个 html 就是一段文本
}
}
return root
// parseStartTag 函数的声明
// ...
// processElement 函数的声明
}
// processVModel 函数的声明
// ...
// processVOn 函数的声明parseStartTag
/src/compiler/parse.js
/**
* 解析开始标签
* 比如: <div id="app">...</div>
*/
function parseStartTag() {
// 先找到开始标签的结束位置 >
const end = html.indexOf('>')
// 解析开始标签里的内容 <内容>,标签名 + 属性,比如: div id="app"
const content = html.slice(1, end)
// 截断 html,将上面解析的内容从 html 字符串中删除
html = html.slice(end + 1)
// 找到 第一个空格位置
const firstSpaceIdx = content.indexOf(' ')
// 标签名和属性字符串
let tagName = '', attrsStr = ''
if (firstSpaceIdx === -1) {
// 没有空格,则认为 content 就是标签名,比如 <h3></h3> 这种情况,content = h3
tagName = content
// 没有属性
attrsStr = ''
} else {
tagName = content.slice(0, firstSpaceIdx)
// content 的剩下的内容就都是属性了,比如 id="app" xx=xx
attrsStr = content.slice(firstSpaceIdx + 1)
}
// 得到属性数组,[id="app", xx=xx]
const attrs = attrsStr ? attrsStr.split(' ') : []
// 进一步解析属性数组,得到一个 Map 对象
const attrMap = parseAttrs(attrs)
// 生成 AST 对象
const elementAst = generateAST(tagName, attrMap)
// 如果根节点不存在,说明当前节点为整个模版的第一个节点
if (!root) {
root = elementAst
}
// 将 ast 对象 push 到栈中,当遇到结束标签的时候就将栈顶的 ast 对象 pop 出来,它两就是一对儿
stack.push(elementAst)
// 自闭合标签,则直接调用 end 方法,进入闭合标签的处理截断,就不入栈了
if (isUnaryTag(tagName)) {
processElement()
}
}parseEnd
/src/compiler/parse.js
/**
* 处理结束标签,比如: <div id="app">...</div>
*/
function parseEnd() {
// 将结束标签从 html 字符串中截掉
html = html.slice(html.indexOf('>') + 1)
// 处理栈顶元素
processElement()
}parseAttrs
/src/compiler/parse.js
/**
* 解析属性数组,得到一个属性 和 值组成的 Map 对象
* @param {*} attrs 属性数组,[id="app", xx="xx"]
*/
function parseAttrs(attrs) {
const attrMap = {}
for (let i = 0, len = attrs.length; i < len; i++) {
const attr = attrs[i]
const [attrName, attrValue] = attr.split('=')
attrMap[attrName] = attrValue.replace(/"/g, '')
}
return attrMap
}generateAST
/src/compiler/parse.js
/**
* 生成 AST 对象
* @param {*} tagName 标签名
* @param {*} attrMap 标签组成的属性 map 对象
*/
function generateAST(tagName, attrMap) {
return {
// 元素节点
type: 1,
// 标签
tag: tagName,
// 原始属性 map 对象,后续还需要进一步处理
rawAttr: attrMap,
// 子节点
children: [],
}
}processChars
/src/compiler/parse.js
/**
* 处理文本
* @param {string} text
*/
function processChars(text) {
// 去除空字符或者换行符的情况
if (!text.trim()) return
// 构造文本节点的 AST 对象
const textAst = {
type: 3,
text,
}
if (text.match(/{{(.*)}}/)) {
// 说明是表达式
textAst.expression = RegExp.$1.trim()
}
// 将 ast 放到栈顶元素的肚子里
stack[stack.length - 1].children.push(textAst)
}processElement
/src/compiler/parse.js
/**
* 处理元素的闭合标签时会调用该方法
* 进一步处理元素上的各个属性,将处理结果放到 attr 属性上
*/
function processElement() {
// 弹出栈顶元素,进一步处理该元素
const curEle = stack.pop()
const stackLen = stack.length
// 进一步处理 AST 对象中的 rawAttr 对象 { attrName: attrValue, ... }
const { tag, rawAttr } = curEle
// 处理结果都放到 attr 对象上,并删掉 rawAttr 对象中相应的属性
curEle.attr = {}
// 属性对象的 key 组成的数组
const propertyArr = Object.keys(rawAttr)
if (propertyArr.includes('v-model')) {
// 处理 v-model 指令
processVModel(curEle)
} else if (propertyArr.find(item => item.match(/^v-bind:(.*)/))) {
// 处理 v-bind 指令,比如 <span v-bind:test="xx" />
processVBind(curEle, RegExp.$1, rawAttr[`v-bind:${RegExp.$1}`])
} else if (propertyArr.find(item => item.match(/^v-on:(.*)/))) {
// 处理 v-on 指令,比如 <button v-on:click="add"> add </button>
processVOn(curEle, RegExp.$1, rawAttr[`v-on:${RegExp.$1}`])
}
// 节点处理完以后让其和父节点产生关系
if (stackLen) {
stack[stackLen - 1].children.push(curEle)
curEle.parent = stack[stackLen - 1]
}
}processVModel
/src/compiler/parse.js
/**
* 处理 v-model 指令,将处理结果直接放到 curEle 对象身上
* @param {*} curEle
*/
function processVModel(curEle) {
const { tag, rawAttr, attr } = curEle
const { type, 'v-model': vModelVal } = rawAttr
if (tag === 'input') {
if (/text/.test(type)) {
// <input type="text" v-model="inputVal" />
attr.vModel = { tag, type: 'text', value: vModelVal }
} else if (/checkbox/.test(type)) {
// <input type="checkbox" v-model="isChecked" />
attr.vModel = { tag, type: 'checkbox', value: vModelVal }
}
} else if (tag === 'textarea') {
// <textarea v-model="test" />
attr.vModel = { tag, value: vModelVal }
} else if (tag === 'select') {
// <select v-model="selectedValue">...</select>
attr.vModel = { tag, value: vModelVal }
}
}processVBind
/src/compiler/parse.js
/**
* 处理 v-bind 指令
* @param {*} curEle 当前正在处理的 AST 对象
* @param {*} bindKey v-bind:key 中的 key
* @param {*} bindVal v-bind:key = val 中的 val
*/
function processVBind(curEle, bindKey, bindVal) {
curEle.attr.vBind = { [bindKey]: bindVal }
}processVOn
/src/compiler/parse.js
/**
* 处理 v-on 指令
* @param {*} curEle 当前被处理的 AST 对象
* @param {*} vOnKey v-on:key 中的 key
* @param {*} vOnVal v-on:key="val" 中的 val
*/
function processVOn(curEle, vOnKey, vOnVal) {
curEle.attr.vOn = { [vOnKey]: vOnVal }
}isUnaryTag
/src/utils.js
/**
* 是否为自闭合标签,内置一些自闭合标签,为了处理简单
*/
export function isUnaryTag(tagName) {
const unaryTag = ['input']
return unaryTag.includes(tagName)
}generate
/src/compiler/generate.js
/**
* 从 ast 生成渲染函数
* @param {*} ast ast 语法树
* @returns 渲染函数
*/
export default function generate(ast) {
// 渲染函数字符串形式
const renderStr = genElement(ast)
// 通过 new Function 将字符串形式的函数变成可执行函数,并用 with 为渲染函数扩展作用域链
return new Function(`with(this) { return ${renderStr} }`)
}genElement
/src/compiler/generate.js
/**
* 解析 ast 生成 渲染函数
* @param {*} ast 语法树
* @returns {string} 渲染函数的字符串形式
*/
function genElement(ast) {
const { tag, rawAttr, attr } = ast
// 生成属性 Map 对象,静态属性 + 动态属性
const attrs = { ...rawAttr, ...attr }
// 处理子节点,得到一个所有子节点渲染函数组成的数组
const children = genChildren(ast)
// 生成 VNode 的可执行方法
return `_c('${tag}', ${JSON.stringify(attrs)}, [${children}])`
}genChildren
/src/compiler/generate.js
/**
* 处理 ast 节点的子节点,将子节点变成渲染函数
* @param {*} ast 节点的 ast 对象
* @returns [childNodeRender1, ....]
*/
function genChildren(ast) {
const ret = [], { children } = ast
// 遍历所有的子节点
for (let i = 0, len = children.length; i < len; i++) {
const child = children[i]
if (child.type === 3) {
// 文本节点
ret.push(`_v(${JSON.stringify(child)})`)
} else if (child.type === 1) {
// 元素节点
ret.push(genElement(child))
}
}
return ret
}结果
在 mount 方法中加一句 console.log(vm.$options.render),打开控制台,刷新页面,看到如下内容,说明编译器就完成了
接下来就会进入正式的挂载阶段,完成页面的初始渲染。
链接
- 配套视频,微信公众号回复:"精通 Vue 技术栈源码原理视频版" 获取
- 精通 Vue 技术栈源码原理 专栏
- github 仓库 liyongning/Vue 欢迎 Star
- github 仓库 liyongning/Lyn-Vue-DOM 欢迎 Star
- github 仓库 liyongning/Lyn-Vue-Template 欢迎 Star
感谢各位的:关注、点赞、收藏和评论,我们下期见。
当学习成为了习惯,知识也就变成了常识。 感谢各位的 关注、 点赞、收藏和评论。
新视频和文章会第一时间在微信公众号发送,欢迎关注:李永宁lyn
文章已收录到 github 仓库 liyongning/blog,欢迎 Watch 和 Star。
|
- 上一条: TypeScript 2.0开启空值的严格检查 2022-03-15
- 下一条: 欢迎体验 | Android 13 开发者预览版 2 2022-03-18
- 手写 Vue 系列 之 Vue1.x 2022-03-14
- vue3,对比 vue2 有什么优点? 2021-09-16
- 30个类手写Spring核心原理之动态数据源切换(8) 2021-12-21
- TiFlash 面向编译器的自动向量化加速 2022-06-28
- 跟我一起学Go系列:Go gRPC 安全认证机制-SSL/TLS认证 2021-07-07